Today is National HIV Testing Day, and one of the most fulfilling conversations to have with persons living with HIV (PLWH) is to share that since the 1980’s, we have made significant progress in the management of the AIDS epidemic. FDA approval of 27 antiretrovirals and 20 fixed dose combination antiretrovirals, increased HIV testing campaigns and funding for HIV care through the Ryan White Comprehensive AIDS Resource Emergency (CARE) Act have made it possible for millions of persons with HIV to live fulfilling lives. Notwithstanding these amazing movements, eliminating HIV remains a moving target as stigma and socioeconomic, racial, age and gender disparities result in inequalities of diagnosis, linkage to and retention in care.
 In 2006, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommended universal HIV screening, which was endorsed by the United States Preventive Services Taskforce (USPSTF) in 2013. Despite these recommendations, 1 in 7 persons living with HIV (PLWH) in the United States are unaware of their diagnosis. When stratified by age, young people between the ages of 13-24 account for 22% of all new HIV diagnoses in the U.S., but 44% of PLWH in this age group are unaware of their diagnosis (the highest percentage among all age groups).
In 2006, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommended universal HIV screening, which was endorsed by the United States Preventive Services Taskforce (USPSTF) in 2013. Despite these recommendations, 1 in 7 persons living with HIV (PLWH) in the United States are unaware of their diagnosis. When stratified by age, young people between the ages of 13-24 account for 22% of all new HIV diagnoses in the U.S., but 44% of PLWH in this age group are unaware of their diagnosis (the highest percentage among all age groups).
HIV testing is available at multiple locations. You can ask your primary care clinician to test you for HIV, but did you know that you can get tested for free or low cost at multiple locations near you? These can be local nonprofits like the Nebraska AIDS Project (NAP), your County Health Department like the (Douglas County STD Clinic). Getting tested for HIV can be quick, easy and confidential – go to bit.ly/NHTD2017 and enter your zip code to find an HIV testing location near you.
 Our Specialty Care Clinic works closely with the Douglas County STD Clinic and NAP. We treat PLWH diagnosed with HIV at these locations and provide pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) for patients who are at risk. Our nurse and case manager Precious Davis BSN, MSN has been very involved with reaching out to our community to spread the message of HIV testing. At an event in the Spring, Precious shared some of these statistics and information on treatment and stigma of HIV care in a poem (pictured here). At that event, 25 people were tested for HIV.
Our Specialty Care Clinic works closely with the Douglas County STD Clinic and NAP. We treat PLWH diagnosed with HIV at these locations and provide pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) for patients who are at risk. Our nurse and case manager Precious Davis BSN, MSN has been very involved with reaching out to our community to spread the message of HIV testing. At an event in the Spring, Precious shared some of these statistics and information on treatment and stigma of HIV care in a poem (pictured here). At that event, 25 people were tested for HIV.
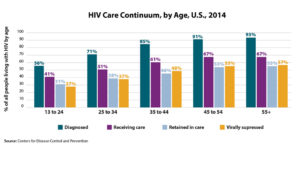 The HIV Care Continuum demonstrates our progress and areas for improvement towards our goal of eliminating HIV. While 85% of persons living with HIV (PLWH) are aware of their diagnosis, less than 50% of these people have achieved viral suppression. PLWH who are not virally suppressed are at risk of transmitting the virus to others, subsequently repeating the cycle of infection. Therefore successful campaigns to end HIV must not only focus on diagnosis and treatment, but also prevention. HIV treatment as prevention for PLWH and Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) for persons without HIV (but are at risk for becoming infected) are very powerful prevention tools that require retention in care. We need to test more people for HIV so that 15% of undiagnosed PLWH are brought into care, but a greater challenge beyond that lies in our ability to retain PLWH engagement in care.
The HIV Care Continuum demonstrates our progress and areas for improvement towards our goal of eliminating HIV. While 85% of persons living with HIV (PLWH) are aware of their diagnosis, less than 50% of these people have achieved viral suppression. PLWH who are not virally suppressed are at risk of transmitting the virus to others, subsequently repeating the cycle of infection. Therefore successful campaigns to end HIV must not only focus on diagnosis and treatment, but also prevention. HIV treatment as prevention for PLWH and Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) for persons without HIV (but are at risk for becoming infected) are very powerful prevention tools that require retention in care. We need to test more people for HIV so that 15% of undiagnosed PLWH are brought into care, but a greater challenge beyond that lies in our ability to retain PLWH engagement in care.
How can YOU help to end the AIDS epidemic? Get tested. Encourage your friends and partners to get tested. If you test positive, get into care with an HIV clinician, and STAY in care. If you are a clinician, screen your patients for HIV, regardless of perceived risk; offer high risk patients PrEP, and commit to keep your patients engaged in care.
 Then it got worse. Around 1 week later, the cough started. The body aches. The headaches. The sore throat. The “influenza-like illness,” or ILI, arrived with no apologies. I thought the virus had done its worst; then, as I made my morning coffee, Wacky Wednesday started. I could not smell it. It seemed strange, but I thought it was just congestion. I took a sip. Hot liquid, tasteless. I rummaged through my kitchen–smelling and tasting noxious things, testing my senses. Garlic? Nothing. Chili Lime seasoning? Nothing. Pepper, salt, ginger? All nothing.
Then it got worse. Around 1 week later, the cough started. The body aches. The headaches. The sore throat. The “influenza-like illness,” or ILI, arrived with no apologies. I thought the virus had done its worst; then, as I made my morning coffee, Wacky Wednesday started. I could not smell it. It seemed strange, but I thought it was just congestion. I took a sip. Hot liquid, tasteless. I rummaged through my kitchen–smelling and tasting noxious things, testing my senses. Garlic? Nothing. Chili Lime seasoning? Nothing. Pepper, salt, ginger? All nothing. For most infections, think the common cold or upper respiratory infections, it seems that the post-infection loss of smell is generally temporary due to the phenomenal plasticity of the olfactory system. In fact, after URI’s, 32-66% of patients will recover their sense of smell spontaneously. For those struggling, training your sniffer can carry significant advantages toward recovering with intentionally smelling various types of odors a few times per day to “retrain” the olfactory system. It’s physical therapy for the nose!
For most infections, think the common cold or upper respiratory infections, it seems that the post-infection loss of smell is generally temporary due to the phenomenal plasticity of the olfactory system. In fact, after URI’s, 32-66% of patients will recover their sense of smell spontaneously. For those struggling, training your sniffer can carry significant advantages toward recovering with intentionally smelling various types of odors a few times per day to “retrain” the olfactory system. It’s physical therapy for the nose! After almost a year of planning, the First Annual Nebraska Antimicrobial Stewardship Summit convened on Friday, June 1st, 2018 in La Vista, NE. This conference is the first of its kind in Nebraska in which information on antimicrobial stewardship in various healthcare settings is the focus of the meeting. The conference center was abuzz with excitement as close to 270 healthcare professionals attended the Summit that included over 130 nurses, 80 pharmacists, and 30 providers. While the majority of the attendees were from Nebraska, healthcare professionals from neighboring states such as Iowa, Kansas, Missouri and South Dakota also attended the Summit.
After almost a year of planning, the First Annual Nebraska Antimicrobial Stewardship Summit convened on Friday, June 1st, 2018 in La Vista, NE. This conference is the first of its kind in Nebraska in which information on antimicrobial stewardship in various healthcare settings is the focus of the meeting. The conference center was abuzz with excitement as close to 270 healthcare professionals attended the Summit that included over 130 nurses, 80 pharmacists, and 30 providers. While the majority of the attendees were from Nebraska, healthcare professionals from neighboring states such as Iowa, Kansas, Missouri and South Dakota also attended the Summit. The morning session continued with presentations from Dr. Diekema (Professor, University of Iowa Carver College of Medicine, pictured to the left) on the Role of the Laboratory in Antimicrobial Stewardship; Drs. Vivekanandan (Associate Professor of Medicine, Creighton University) and Horne (Assistant Professor of Medicine, Creighton University) on “Is Antibiotic Stewardship the Answer to C. difficile”; and Kate Tyner, RN, CIC (Nurse Coordinator, Nebraska ASAP and ICAP) on the “Role of the Infection Preventionist in Antimicrobial Stewardship”. The morning session concluded with a presentation from Drs. Tierney and Pedati (Medical Epidemiologist, Nebraska DHHS) on “Public Health Support for Antimicrobial Stewardship” in which they discussed the state MDRO outbreak detection and management protocols as well as the state antimicrobial susceptibility registry and antibiogram.
The morning session continued with presentations from Dr. Diekema (Professor, University of Iowa Carver College of Medicine, pictured to the left) on the Role of the Laboratory in Antimicrobial Stewardship; Drs. Vivekanandan (Associate Professor of Medicine, Creighton University) and Horne (Assistant Professor of Medicine, Creighton University) on “Is Antibiotic Stewardship the Answer to C. difficile”; and Kate Tyner, RN, CIC (Nurse Coordinator, Nebraska ASAP and ICAP) on the “Role of the Infection Preventionist in Antimicrobial Stewardship”. The morning session concluded with a presentation from Drs. Tierney and Pedati (Medical Epidemiologist, Nebraska DHHS) on “Public Health Support for Antimicrobial Stewardship” in which they discussed the state MDRO outbreak detection and management protocols as well as the state antimicrobial susceptibility registry and antibiogram. During lunch, Summit attendees had the opportunity for roundtable discussions with
During lunch, Summit attendees had the opportunity for roundtable discussions with  Education in antimicrobial stewardship continues in the afternoon with breakout sessions in the Acute and Ambulatory Track and the Post-Acute and Long-Term Care Track at the Summit. Dr. Bergman (Pharmacy Coordinator, Antimicrobial Stewardship Program, Nebraska Medicine, pictured to the left) started the acute and ambulatory session with his presentation on “Regulatory Requirements for Hospitals and Outpatient Antimicrobial Stewardship”. This was followed by presentations from Dr. Van Schooneveld (Medical Director, Antimicrobial Stewardship Program, Nebraska Medicine) on “Antimicrobial Stewardship Interventions in Acute Care Hospitals”; Dr. Kuper (Senior Clinical Manager, Infectious Diseases, Vizient) on “Antibiotic Stewardship Metrics: How Do You Measure Up?”; and Drs. Marcelin (Associate Medical Director, Antimicrobial Stewardship Program, Nebraska Medicine) and Green Hines (Medical Director, Antimicrobial Stewardship Program, Children’s Hospital & Medical Center) on “Antimicrobial Stewardship in the Outpatient Setting (#OutptASP)”. The session was well attended and appreciated by Summit attendees.
Education in antimicrobial stewardship continues in the afternoon with breakout sessions in the Acute and Ambulatory Track and the Post-Acute and Long-Term Care Track at the Summit. Dr. Bergman (Pharmacy Coordinator, Antimicrobial Stewardship Program, Nebraska Medicine, pictured to the left) started the acute and ambulatory session with his presentation on “Regulatory Requirements for Hospitals and Outpatient Antimicrobial Stewardship”. This was followed by presentations from Dr. Van Schooneveld (Medical Director, Antimicrobial Stewardship Program, Nebraska Medicine) on “Antimicrobial Stewardship Interventions in Acute Care Hospitals”; Dr. Kuper (Senior Clinical Manager, Infectious Diseases, Vizient) on “Antibiotic Stewardship Metrics: How Do You Measure Up?”; and Drs. Marcelin (Associate Medical Director, Antimicrobial Stewardship Program, Nebraska Medicine) and Green Hines (Medical Director, Antimicrobial Stewardship Program, Children’s Hospital & Medical Center) on “Antimicrobial Stewardship in the Outpatient Setting (#OutptASP)”. The session was well attended and appreciated by Summit attendees. Equally well attended is the post-acute and long-term care session that was opened with a presentation from Dr. Crnich (Chief of Medicine and Hospital Epidemiologist, Williams S. Middleton VA Hospital, pictured to the left) on “Regulatory Requirements for Post-Acute and Long-Term Care Antimicrobial Stewardship Programs”. This afternoon session continued with Dr. Ashraf (Co-Medical Director, Nebraska ASAP and Medical Director, Nebraska ICAP) speaking on “Antimicrobial Stewardship Implementation in Post-Acute and Long-Term Care Facilities”; Dr. Crnich on “Management of Common Infections in Long-Term Care Facilities”. The session concluded with a presentation from Tammi Schaffart, RN (Infection Control Nurse and QAPI Coordinator, Douglas County Health Center) and Dr. Ortmeier (Consultant Pharmacist Team Lead, Community Pharmacy Services) on the “Role of Nurses and Consultant Pharmacists in Antibiotic Stewardship in Post-Acute and Long-Term Care Facilities”.
Equally well attended is the post-acute and long-term care session that was opened with a presentation from Dr. Crnich (Chief of Medicine and Hospital Epidemiologist, Williams S. Middleton VA Hospital, pictured to the left) on “Regulatory Requirements for Post-Acute and Long-Term Care Antimicrobial Stewardship Programs”. This afternoon session continued with Dr. Ashraf (Co-Medical Director, Nebraska ASAP and Medical Director, Nebraska ICAP) speaking on “Antimicrobial Stewardship Implementation in Post-Acute and Long-Term Care Facilities”; Dr. Crnich on “Management of Common Infections in Long-Term Care Facilities”. The session concluded with a presentation from Tammi Schaffart, RN (Infection Control Nurse and QAPI Coordinator, Douglas County Health Center) and Dr. Ortmeier (Consultant Pharmacist Team Lead, Community Pharmacy Services) on the “Role of Nurses and Consultant Pharmacists in Antibiotic Stewardship in Post-Acute and Long-Term Care Facilities”. Track shared their thoughts. Dr. Crnich said it takes a team to establish a stewardship program while Dr. Ashraf (pictured to the left) echoed a similar sentiment that no one is alone in this journey. Tammi emphasized to the many nurses in the audience the importance of documentation to show their efforts for the numerous clinical activities they performed in nursing facilities, including antimicrobial stewardship. Dr. Ortmeier stressed the importance of persistence and the need to continue to ‘keep at it’ for eventual success.
Track shared their thoughts. Dr. Crnich said it takes a team to establish a stewardship program while Dr. Ashraf (pictured to the left) echoed a similar sentiment that no one is alone in this journey. Tammi emphasized to the many nurses in the audience the importance of documentation to show their efforts for the numerous clinical activities they performed in nursing facilities, including antimicrobial stewardship. Dr. Ortmeier stressed the importance of persistence and the need to continue to ‘keep at it’ for eventual success. We genuinely appreciate the support Summit attendees expressed. It is our hope that this type of Summit will continue annually in the future and that new topics and updated contents in antimicrobial stewardship will be presented. Additionally, we hope to make many more connections with healthcare professionals in Nebraska and neighboring states to improve the care and safety of our patients and residents by improving prescribing of this precious resource, antimicrobials, through antimicrobial stewardship.
We genuinely appreciate the support Summit attendees expressed. It is our hope that this type of Summit will continue annually in the future and that new topics and updated contents in antimicrobial stewardship will be presented. Additionally, we hope to make many more connections with healthcare professionals in Nebraska and neighboring states to improve the care and safety of our patients and residents by improving prescribing of this precious resource, antimicrobials, through antimicrobial stewardship. PADDLE Trial4: A pilot, non-blinded, non-randomized, non-parallel, 48 week trial in Argentina. This trial enrolled 20 patients that were naïve to ART, viral loads ranging from 5,000 to 100,000 copies/mL and CD4+ greater 200cells/mm3. The participants in this trial were primarily assessed to see the rate of success at achieving HIV levels of 50 copies/mL or less at 48 weeks. At 48 weeks, 18/20 (90%) patients reached the viral levels desired, including 4 patients with viral loads greater than 100,000 (albeit to protocol). Additionally, safety and efficacy of this dual therapy was analyzed in this trial. Only one protocol failure developed; however, participants achieved levels less than 50 copies/mL from Week 4-24 and developed no resistance to any of the agents.
PADDLE Trial4: A pilot, non-blinded, non-randomized, non-parallel, 48 week trial in Argentina. This trial enrolled 20 patients that were naïve to ART, viral loads ranging from 5,000 to 100,000 copies/mL and CD4+ greater 200cells/mm3. The participants in this trial were primarily assessed to see the rate of success at achieving HIV levels of 50 copies/mL or less at 48 weeks. At 48 weeks, 18/20 (90%) patients reached the viral levels desired, including 4 patients with viral loads greater than 100,000 (albeit to protocol). Additionally, safety and efficacy of this dual therapy was analyzed in this trial. Only one protocol failure developed; however, participants achieved levels less than 50 copies/mL from Week 4-24 and developed no resistance to any of the agents. GEMINI I1 and GEMINI II2: Two, nearly identical large phase III, randomized, double-blinded, multinational, multicenter, parallel studies that enrolled 719 and 722 ART naïve participants. The primary purposes of these studies were to assess the percentage of subjects with viral loads between 1,000-100,000 copies/mL and CD4>200/mm3 who achieved viral suppression (HIV VL<50 copies/mL) at Week 48. Preliminary results for these trials are expected to be released in the summer of 2018 and study completion is scheduled for March 2020.
GEMINI I1 and GEMINI II2: Two, nearly identical large phase III, randomized, double-blinded, multinational, multicenter, parallel studies that enrolled 719 and 722 ART naïve participants. The primary purposes of these studies were to assess the percentage of subjects with viral loads between 1,000-100,000 copies/mL and CD4>200/mm3 who achieved viral suppression (HIV VL<50 copies/mL) at Week 48. Preliminary results for these trials are expected to be released in the summer of 2018 and study completion is scheduled for March 2020. Content provided by Freddy Orellana, UNMC PharmD Candidate ’18, and Joshua Havens PharmD
Content provided by Freddy Orellana, UNMC PharmD Candidate ’18, and Joshua Havens PharmD Dr. M. Salman Ashraf, MBBS is an Associate Professor of Medicine and Medical Director of the Nebraska Infection Control Assessment and Promotion Program (ICAP). He also Co-Directs the Nebraska Antimicrobial Stewardship Assessment and Promotion (ASAP) Program with Dr. Trevor Van Schooneveld, and is Associate Medical Director Infection Control and Epidemiology at Nebraska Medicine. Dr. Ashraf’s clinical and research interests in antimicrobial stewardship and infection control in long-term care facilities (LCTF) have led to countless national speaker invitations and significant research funding granted to study antimicrobial stewardship and infection control in LCTF.
Dr. M. Salman Ashraf, MBBS is an Associate Professor of Medicine and Medical Director of the Nebraska Infection Control Assessment and Promotion Program (ICAP). He also Co-Directs the Nebraska Antimicrobial Stewardship Assessment and Promotion (ASAP) Program with Dr. Trevor Van Schooneveld, and is Associate Medical Director Infection Control and Epidemiology at Nebraska Medicine. Dr. Ashraf’s clinical and research interests in antimicrobial stewardship and infection control in long-term care facilities (LCTF) have led to countless national speaker invitations and significant research funding granted to study antimicrobial stewardship and infection control in LCTF.
 Dr. Bradley Britigan, MD is the Dean of the University of Nebraska Medical Center College of Medicine, and Department of Internal Medicine Stokes-Shackleford Professor. Despite his busy administrative duties, Dr. Britigan still finds time to practice clinically at the VA hospital, attends on our General ID teaching service, and contributes to our Division research meetings. His research interests include the pathogenesis of Pseudomonas spp. and Mycobacteria spp. Lung Infections, and Microbial Iron Metabolism as a target for Novel Antimicrobial Therapies.
Dr. Bradley Britigan, MD is the Dean of the University of Nebraska Medical Center College of Medicine, and Department of Internal Medicine Stokes-Shackleford Professor. Despite his busy administrative duties, Dr. Britigan still finds time to practice clinically at the VA hospital, attends on our General ID teaching service, and contributes to our Division research meetings. His research interests include the pathogenesis of Pseudomonas spp. and Mycobacteria spp. Lung Infections, and Microbial Iron Metabolism as a target for Novel Antimicrobial Therapies. is a Professor in the Department of Pathology and Microbiology, Medical Director of the Clinical Microbiology Laboratory and Research Vice Chair of the Department of Pathology and Microbiology. Our Division collaborates closely with Dr. Fey and the microbiology lab on implementation and improvement of diagnostic testing to improve clinical care. His research interests include the Metabolism and Pathogenesis of staphylococcal infections. Just recently, Dr. Fey was honored with the 2017-2018 Outstanding Graduate Student Educator award in the department of Pathology & Microbiology at UNMC.
is a Professor in the Department of Pathology and Microbiology, Medical Director of the Clinical Microbiology Laboratory and Research Vice Chair of the Department of Pathology and Microbiology. Our Division collaborates closely with Dr. Fey and the microbiology lab on implementation and improvement of diagnostic testing to improve clinical care. His research interests include the Metabolism and Pathogenesis of staphylococcal infections. Just recently, Dr. Fey was honored with the 2017-2018 Outstanding Graduate Student Educator award in the department of Pathology & Microbiology at UNMC. is an Infectious Diseases-Trained Pharmacist with primary focus in the Specialty Care Clinic (SCC) which serves persons living with HIV (PLWH) in our Omaha and neighboring communities. He is leads the management team for the Ryan Wite AIDS Drug Assistance Program (ADAP) for the state of Nebraska. In his clinical role at the SCC, Dr. Havens not only facilitates discussions with clinicians and PLWH about complex medication issues, but runs a clinic for HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP). This has fueled his primary research focus on the prevention of HIV as well as developing novel adherence strategies to keep PLWH healthy. He collaborates in these projects with Drs. Sara Bares and Susan Swindells.
is an Infectious Diseases-Trained Pharmacist with primary focus in the Specialty Care Clinic (SCC) which serves persons living with HIV (PLWH) in our Omaha and neighboring communities. He is leads the management team for the Ryan Wite AIDS Drug Assistance Program (ADAP) for the state of Nebraska. In his clinical role at the SCC, Dr. Havens not only facilitates discussions with clinicians and PLWH about complex medication issues, but runs a clinic for HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP). This has fueled his primary research focus on the prevention of HIV as well as developing novel adherence strategies to keep PLWH healthy. He collaborates in these projects with Drs. Sara Bares and Susan Swindells. , MD is a Professor of Internal Medicine, and Director of the Transplant Infectious Diseases practice group at UNMC ID. He also holds board certification in Critical Care Medicine and has a special interest in infections occurring in the intensive care unit. Dr. Kalil is nationally and internationally recognized for his work in the field of severe sepsis, hospital acquired and ventilator acquired pneumonia, and was the first author and writing group leader of the recent IDSA/American Thoracic Society Guidelines on Management of Adults With Hospital-acquired and Ventilator-associated Pneumonia. Dr. Kalil has acquired numerous grants with funding to study cytomegalovirus and other infections associated with solid organ transplantation.
, MD is a Professor of Internal Medicine, and Director of the Transplant Infectious Diseases practice group at UNMC ID. He also holds board certification in Critical Care Medicine and has a special interest in infections occurring in the intensive care unit. Dr. Kalil is nationally and internationally recognized for his work in the field of severe sepsis, hospital acquired and ventilator acquired pneumonia, and was the first author and writing group leader of the recent IDSA/American Thoracic Society Guidelines on Management of Adults With Hospital-acquired and Ventilator-associated Pneumonia. Dr. Kalil has acquired numerous grants with funding to study cytomegalovirus and other infections associated with solid organ transplantation. , MPH is an Associate Professor of Medicine and Fellow in the Infectious Diseases Society of America (FIDSA). He is the Director of International Programs and Innovation, at the Global Center for Health Security and has led several teams to countries in West Africa focusing on Public Health Emergency Preparedness. Dr. Lawler, a former White House Homeland Security Council biodefense policy director, has national expertise on Biosecurity and viral hemorrhagic fevers, and is the current Director of Clinical and Biodefense Research at the National Strategic Research Institute.
, MPH is an Associate Professor of Medicine and Fellow in the Infectious Diseases Society of America (FIDSA). He is the Director of International Programs and Innovation, at the Global Center for Health Security and has led several teams to countries in West Africa focusing on Public Health Emergency Preparedness. Dr. Lawler, a former White House Homeland Security Council biodefense policy director, has national expertise on Biosecurity and viral hemorrhagic fevers, and is the current Director of Clinical and Biodefense Research at the National Strategic Research Institute.
 Dr. Uriel Sandkovsky, MD is an Associate Professor of Medicine and Medical Director of Employee Health at UNMC. He attends on the Transplant Infectious Diseases service. His research interests include cardiac device infections and viral infections in transplantation.
Dr. Uriel Sandkovsky, MD is an Associate Professor of Medicine and Medical Director of Employee Health at UNMC. He attends on the Transplant Infectious Diseases service. His research interests include cardiac device infections and viral infections in transplantation.

Recent Comments